– ELEMTENTS –
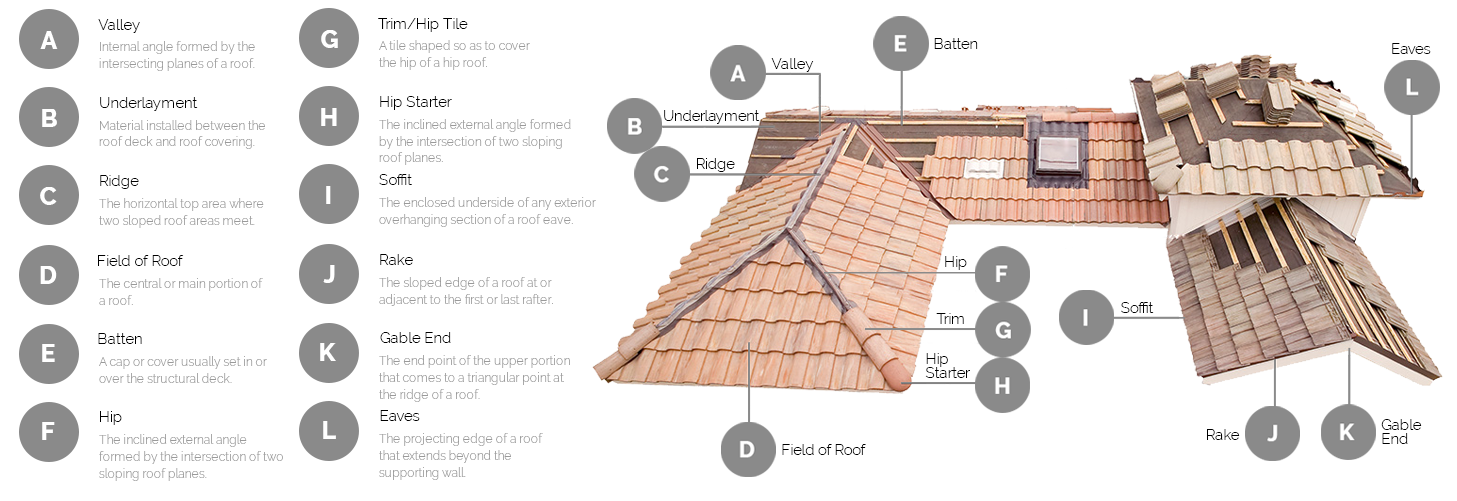
Valleys are internal angles formed by the intersecting planes of a roof, or sections caused by the slope of a roof and a wall.
Underlayment is an asphalt-saturated felt or other sheet material that is installed between the roof deck and roof covering, usually used in a steep-slope roof construction.
The ridge of a sloped roof system is the horizontal top area where two sloped roof areas meet.
The field of roof is the central or main portion of the roof; this excludes the perimeter and flashing.
The batten is a cap or cover in a metal roof, a metal closure set over, or a small piece covering the joint between adjacent metal panels.
The hip is the inclined external angle formed by the intersection of two sloping roof planes.
The trim/hip tile is a tile shaped so as to cover the hip of a hip roof.
The hip starter is the starting point of the inclined external angle formed by the intersection of two sloping roof planes. This runs from the ridge to the eaves.
A skylight is a transparent or translucent item that is designed to admit light. This is typically set over a curbed opening in the roof.
Flashings are pieces of metal or roll roofing used to prevent the seepage of water into a building around any intersection or projection in a roof such as vent pipes, chimneys, adjoining walls, dormers and valleys. Galvanized metal flashing should be minimum 26-gauge.
A soffit is the enclosed underside of any exterior overhanging section of a roof eave.
A rake is the sloped edge of a roof at or adjacent to the first or last rafter.
The gable end is the end point of the upper portion of a sidewall that comes to a triangular point at the ridge of a sloping roof.
Eaves are the projecting edge of a roof that extends beyond the supporting wall.
Three Locations to Service All of
Southern California
We Deliver! Check Out Our Wide Selection of Tile
Call Us Today to find a assortment of tile
From 1 Piece to 1000 Pieces
CLASSIC Roof Tile
What Makes Classic Tile Different Then The Rest
Tiles in Stock
Positive Reviews
Years in Business
Comp. Projects
